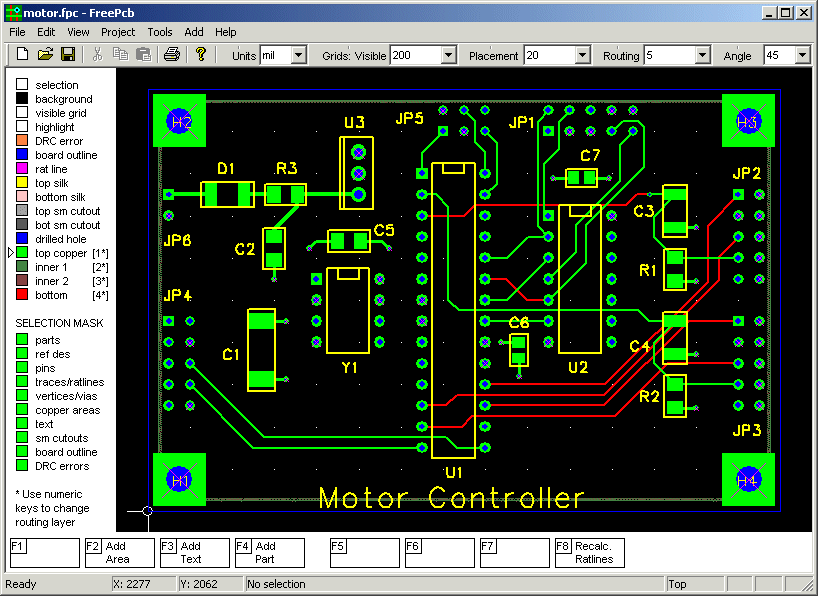
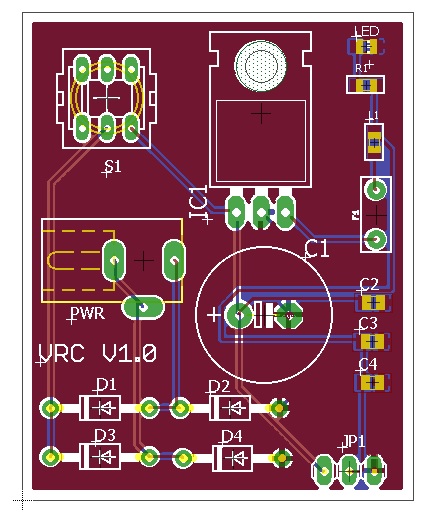
Eagle Pcb Layout Software
- Eagle Pcb Layout Software Download
- Eagle Pcb Layout Software Download
- Pcb Layout Software Comparison
- Eagle Pcb Design Software Tutorial
DesignSpark PCB is a free software package for schematic capture and PCB layout. The software consists of schematic entry and PCB layout and the link between them is very easy. The libraries for components are aligned with RSComponents. It can be easily interfaced with other tools like LTSpice, Tina and Eagle.
- DipTrace - PCB Design software. EDA/CAD package with autorouter, Schematic Capture multi-level hierarchy, real-time DRC, 3D Preview/export, Gerber output and comprhensive component and pattern libraries.
- The Eagle PCB design software is available in three:. Eagle free. Eagle standard. Eagle premium. The eagle free version as you may already be aware is a freeware version that is not paid for. It can be used to capture schematics and the layout of the Printed Circuit Board.
- San Francisco Circuits ultimate PCB design software comparison comprehensively reviews the top 6 PCB design tools in the most complete guide available. CAD programs reviewed include DipTrace, Eagle, KiCAD, OrCAD, PADS & Altium Designer.
- PCB layout and schematic editing tools, library content, and community-driven features. Download Free Version of EAGLE Limited version for hobbyists including 2 schematic sheets, 2 signal layers, and an 80cm 2 (12.4in 2 ) board area.
- How to Design Schematic Diagrams and PCB Layout using Eagle from Cadsoft. This is a quick overview on how to design Schematic Diagrams and Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design Using Eagle.
Introduction
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of every electronic gizmo out there. They're not flashy like those microprocessors, or abundant like resistors, but they're essential to making all components in a circuit connect together just right.
We LOVE designing PCBs here at SparkFun. It's a love that we want to spread. It's a skill that benefits electronics enthusiasts of every caliber. Through this and a series of tutorials, we'll explain how to design a PCB using EAGLE -- the same software we use to design all of our PCBs.
This first tutorial goes over how to install the software, and tailor-fit its interface and support files.
Why EAGLE?
EAGLE is one of many PCB CAD softwares out there. So you might ask: 'What makes EAGLE so special?' We're fond of EAGLE for a few reasons in particular:
- Cross-platform -- EAGLE can run on anything: Windows, Mac, even Linux. This is a feature not too many other PCB design softwares can boast.
- Lightweight -- EAGLE is about as svelte as PCB design software gets. It requires anywhere from 50-200MB of disk space (compared to the 10+GB more advanced tools might require). The installer is about 25MB. So you can go from download to install to making a PCB in minutes.
- Free/Low-Cost -- The freeware version of EAGLE provides enough utility to design almost any PCB in the SparkFun catalog. An upgrade to the next license tier (if you want to make a profit off your design) costs at least two orders of magnitude less than most high-end tools.
- Community support -- For those reasons, and others, EAGLE has become one of the go-to tools for PCB design in the hobbyist community. Whether you want to study the design of an Arduino board or import a popular sensor into your design, somebody has probably already made it in EAGLE and shared it.
Of course, EAGLE has its drawbacks too. More powerful PCB design tools out there might have a better autorouter, or nifty tools like simulators, programmers, and 3D viewers. For us though, EAGLE has everything we need to design simple-to-intermediate PCBs. It's an excellent place to start if you've never designed a PCB before.
Recommended Reading
Here are a few tutorial and concepts you may want to familiarize yourself with before dropping down into this rabbit hole:
Download, Install, Run
EAGLE is available on Cadsoft's (the developer company) download page. Grab the most recent version that matches your operating system (the software is available for Windows, Mac and Linux). It's a relatively light download -- about 45MB.
EAGLE installs just like any old program, it'll self extract and then present you with a series of dialogs to configure the installation.
Licensing EAGLE
On the last screen of the installation process, you should be presented with a window like this:
One of our favorite things about EAGLE is that it can be used for free! There are a few limitations to be aware of when using the free version:
- Your PCB design is limited to a maximum size of 100 x 80mm (3.94 x 3.15in). 12.4 in2 of PCB real estate, which is still pretty darn big. Even if you're designing a big 'ol Arduino shield, you'll still be well under the maximum size.
- Only two signal layers allowed. If you need more layers check into the Hobbyist or Standard licenses.
- Can't make multiple sheets in your schematic editor.
- Limited to email or forum support.
- For non-profit use only. If you're going to go out and sell your design, maybe check into the 'Light' version of the software.
Those limitations still make EAGLE an amazing piece of software. Engineers here at SparkFun could design 99% of our boards using the freeware version, if not for that pesky non-profit stipulation. You still have access to all phases of the EAGLE software, including the Autorouter.
If you need to upgrade your license there are a few versions available. Most licenses are still incredibly low priced (in comparing to the other stuff out there).
Exploring the Control Panel
The first time you open up EAGLE, you should be presented with the Control Panel view. The Control Panel is the 'homebase' for Eagle, it links together all of the other modules in the software.
You can explore the six separate trees in the control panel, which highlight separate functions of the software:
- Libraries -- Libraries store parts, which are a combination of schematic symbol and PCB footprint. Libraries usually contain a group of related parts, e.g. the atmel.lbr stores a good amount of Atmel AVR devices, while the 74xx-us.lbr library has just about every TTL 74xx series IC there is.
- Design Rules (DRU) -- Design rules are a set of rules your board design must meet before you can send it off to the fab house. In this tree you'll find DRU files, which are a a pre-defined set of rules.
- User Language Programs (ULPs) -- ULPs are scripts written in EAGLE's User Language. They can be used to automate processes like generating bill of materials (bom.ulp), or importing a graphic (import-bmp.ulp).
- Scripts (SCR) -- Script files can be used to customize the EAGLE user interface. In one click you can set the color scheme and assign key bindings.
- CAM Jobs (CAM) -- CAM jobs can be opened up by the CAM processor to aid in the creation of gerber files.
- Projects -- This is where each of your projects are organized into a single project folder. Projects will include schematic, board design, and possibly gerber files.
If you select a file in a tree, information about it will appear in the right-hand portion of the window. This is a great way to explore libraries, project designs (EAGLE comes with some fun examples), or to get a good overview of what a script's purpose is.
Using the SparkFun Libraries
Included with EAGLE is an impressive list of part libraries, which you can explore in the Control Panel view. There are hundreds of libraries in here, some devoted to specific parts like resistors, or NPN transistors, others are devoted to specific manufacturers. This is an amazing resource! But it can also be a bit overwhelming. Even if you just want to add a simple through-hole electrolytic capacitor, there are dozens of libraries and parts to sort through to find the right thing.
Instead of using the hundreds of default libraries, you can use the SparkFun EAGLE Libraries, which are filtered down to only include the parts that we've used in designs ourselves. And they're constantly updated with new parts we've discovered.
Here's how you can install and use the SparkFun libraries instead of (or in addition to) the default ones:
Step 1: Download the SparkFun Libraries
The most recent version of the libraries can always be found in the GitHub repository. For help using GitHub, check out our Using GitHub tutorial. Basically, all you'll need to do from the main repository page is click 'Download ZIP'.
Save the ZIP file somewhere handy. Then extract the folder -- don't forget where it is!
Step 2: Updating the Directories Window
Back to the EAGLE Control Panel window now. Go to the 'Options' menu and then select 'Directories'. This is a list of computer directories where EAGLE looks when it populates all six objects in the tree view..including libraries.
In the 'Libraries' box is where we'll add a link to the directory where the SparkFun EAGLE libraries are stored. There are a few options here. If you'd like to keep the default libraries and add the SparkFun library, add a semicolon (;) after '$EAGLEDIRlbr', and paste the SparkFun EAGLE Libraries directory location after that.
Note: Mac and Linux users should place a colon (:) between directories instead of the semicolon.
Step 3: 'Using' Libraries
Now, when you go back and look at the 'Libraries' tree, there should be two folders included, one of which should be our SparkFun Eagle Libraries. The last step is to tell EAGLE that, for now at least, we don't want to use the default libraries. To do this, right click on the 'lbr' folder, and select 'Use none'.
Then, right-click on the 'SparkFun-Eagle-Libraries-master' folder, and select 'Use all'. Then check the libraries in each of the two folders. Next to them should be either a grey or green dot. A green dot next to a library means it's in use, a grey dot means it's not. Your libraries tree should look a little something like this:
If you've created library parts that you would like to share with SparkFun to include in our Eagle library, visit this tutorial to see how.
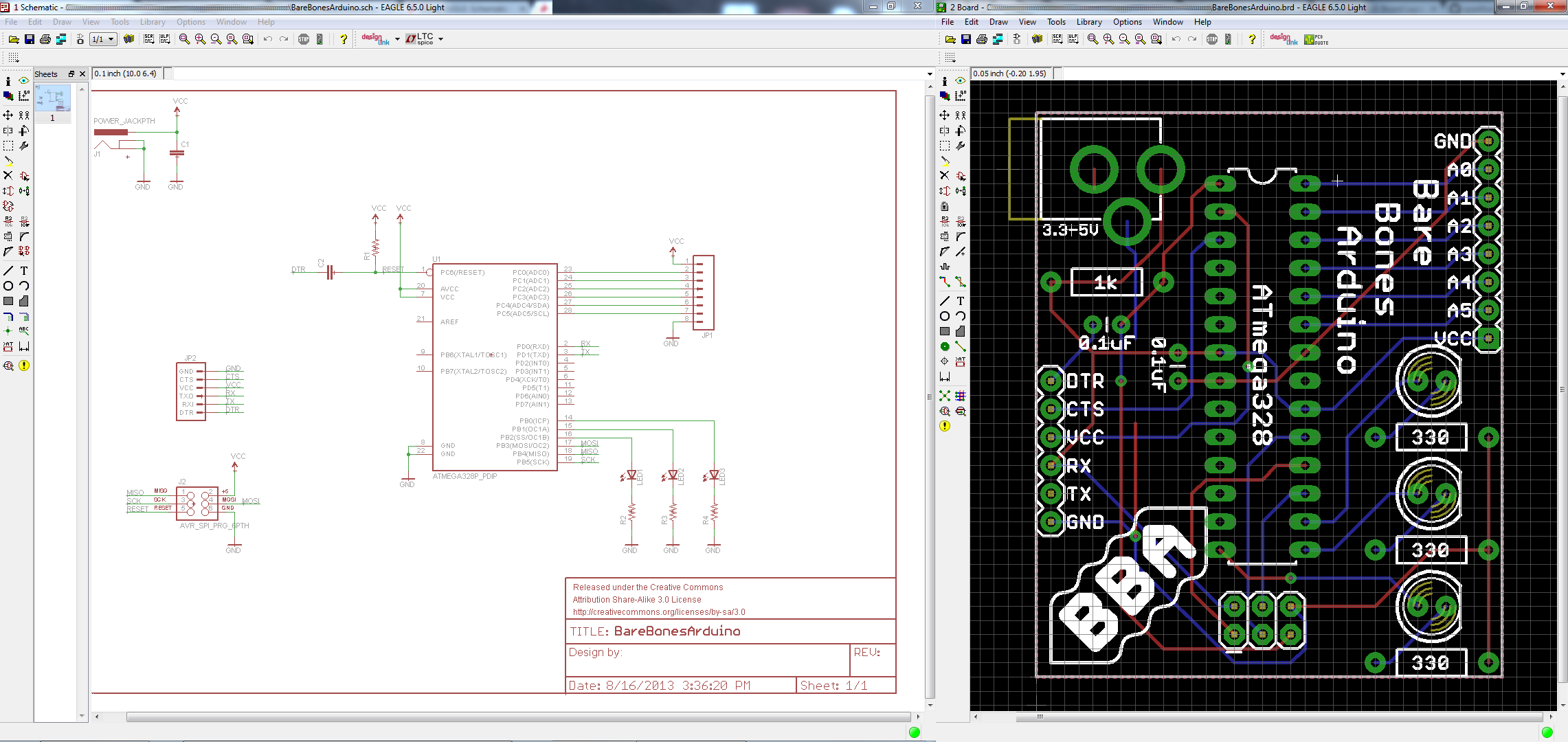
Opening a Project and Explore
EAGLE is packaged with a handful of nifty example PCB designs. Open one up by expanding the 'Projects' tree. From there, under the 'examples' folder open up the 'arduino' project by double-clicking the red folder (or right-clicking and selecting 'Open project'). Game of thrones mod ckii. Note that, in this view, project folders are red and regular folders are the standard yellow.
Opening the project should cause two more EAGLE windows to spawn: the board and schematic editors. These are the yin and the yang of EAGLE. They should be used together to create the finished product that is a functional PCB design.
The schematic editor (on the left above) is a collection of red circuit symbols which are interconnected with green nets (or wires). A project's schematic is like the comments in a program's code. It helps tell the story of what the board design actually does, but it doesn't have much influence on the end product. Parts in a schematic aren't precisely measured, they're laid out and connected in a way that's easy to read, to help you and others understand what's going on with the board design.
The board editor is where the real magic happens. Here colorful layers overlap and intersect to create a precisely measured PCB design. Two copper layers -- red on top, blue on the bottom -- are strategically routed to make sure different signals don't intersect and short out. Yellow circles (on this design, but they're more often green) called 'vias' pass a signal from one side to the other. Bigger vias allow for through-hole parts to be inserted and soldered to the board. Other, currently hidden, layers expose copper so components can be soldered to it.
Keep Both Windows Open!
Both of these windows work hand-in-hand. Any changes made to the schematic are automatically reflected in the board editor. Whenever you're modifying a design it's important to keep both windows open at all times.
If, for instance, you closed the board window of a design, but continued to modify a schematic. The changes you made to the schematic wouldn't be reflected in the board design. This is bad. The schematic and board design should always be consistent. It's really painful to backtrack any changes in an effort to reattain consistency. Always keep both windows open!
There are a few ways to tell if you don't have consistency between windows. First, there's a 'dot' in the lower-right hand corner of both windows. If the dot is green, everything is groovy. If the dot is magenta, a window's probably closed that shouldn't be. Second, and more obvious, if you close either of the two windows a big, huge warning should pop up in the other:
If you see that warning STOP doing anything, and get the other window back open. Gta san andreas download pc windows xp. The easy way to get either a board or schematic window back open is by clicking the 'Switch to board/schematic' icon -- / (also found under the 'File' menu).
Navigating the View
This is a subject that's usually glazed over, but it's important to know how to navigate around both of these windows.
To move around within an editor window, a mouse with a scroll wheel comes in very handy. You can zoom in and out by rotating the wheel forward and backward. Pressing the wheel down, and moving the mouse allows you to drag the screen around.
If you're stuck without a three-button mouse, you'll have to resort to the view options to move around the editor views. All of these tools are located near the middle of the top toolbar, or under the 'View' menu. The zoom in -- -- and zoom out -- -- tools are obviously handy. So is the 'Zoom select' tool -- -- which alters the view to your selection. But really, if you're serious about using EAGLE..get a mouse!
Configuring the UI
EAGLE's user interface is highly customizable. Anything from the background color, to layer colors, to key bindings can be modified to fit your preference. Better tailoring your interface can make designing a PCB much easier. On this page we'll talk about how we at SparkFun prefer to customize our UI. None of these steps are required. Customize your UI as you see fit. These are just the settings that we've grown accustomed to.
Setting the Background Color
The first adjustment we always make to the UI is the background color of the board editor. The standard white background doesn't always meld very well with the array of colored layers required for board design. Instead, we usually opt for a black background.
To change the background color, go up to the 'Options' menu and select 'User interface'.
Inside the 'Layout' box you can set the background to black, white, or a specific color.
Watch Dragon Ball Z and Download Dragon Ball Z in high quality. Various formats from 480p upto 1080p. HTML5 available for mobile devices. Jan 19, 2016 Watch Dragon Ball English Dubbed Online. Dragon Ball Episode 153 English Dubbed Watch Now!!! Dragon Ball Dubbed Episodes List. Dragon Ball Episode 153 English Dubbed January 19, 2016. Dragon Ball Episode 152 English Dubbed January 19, 2016. Dragon Ball Episode 151 English Dubbed January 19, 2016. Watch Dragon Ball Super, Dragon Ball Z, Dragon Ball GT Episodes Online for Free. English Subbed and dubbed anime streaming DB DBZ DBGT DBS episodes and movies HQ Streaming. Free Episodes Online. Watch Dragon Ball Z Online on Putlocker. Put locker is the way to watch Dragon Ball Z movie in HD. Watch Dragon Ball Z in HD. Dragon ball z streaming english.
There are other options in this box to be explored, but you may want to hold off on adjusting most until you have more experience with the software.
Adjusting the Grid
Another UI improvement we like to make in the board editor is turning the grid on. Dimensions and sizes are so important to the design of your PCB, having some visible reminders of size can be very helpful. To turn the grid view on, click the icon near the top-left corner of the board window (or go to the 'View' menu and select 'Grid').
Switch the 'Display' radio button over to 'On'. We'll also make the grid a bit less fine by setting the 'Size' to 100 mil (0.1') and 'Alt' to 50 mil (0.05').
Running Scripts
Scripts are a much more streamlined way to quickly configure your interface. With one click of the button, you can automatically set up all of your colors and key binds. Script files can also be shared, and run by anyone. Running the SparkFun EAGLE script will get your UI to exactly match ours.
Eagle Pcb Layout Software Download
First, click here to download the script (in a zip folder). Unzip the 'spk.scr' file to a location you'll remember.
Then you'll need to run the script. In the board window click on the Script icon -- (or go to 'File' then 'Execute Script'). In the file browser, select the 'spk.scr' file you just downloaded and unzipped.
This should automatically set up your color scheme to look a little something like this:
This UI setup is presents a nice logical view of the layers. The important copper layers are very visible, but distinct (red on top, blue on bottom, green for vias), and the silkscreen is white as it is on most PCB designs.
All of these colored layers will make more sense as you continue to use and explore EAGLE.
SparkFun Custom Eagle Settings
To find SparkFun's most up-to-date script, and other useful files, check out our EAGLE settings repository hosted on GitHub!
Resources and Going Further
If you've got EAGLE set up, and you're chomping at the bit to start designing a PCB, your next step should be over to our 2-part Using EAGLE tutorials: Using EAGLE: Schematic and Using EAGLE: Board Layout. That pair of tutorials will explain how to go from a schematic design, to laying out and routing a PCB, to generating gerber files and sending them to a fab house.
Or here are some other tutorials in our EAGLE series:
- How to Create SMD PCBs -- This should logically follow the PTH EAGLE tutorial. It's a bit more advanced and fast-paced.
- How to Create SMD Footprints -- If you want to create unique parts in a library, check out this tutorial.
- Making Custom Footprints in EAGLE -- Another footprint-making tutorial. This one details a unique process for making a custom 1:1 footprint.
| Developer(s) | Autodesk (previously CadSoft Computer) |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1988; 31 years ago |
| Stable release | 9.4.2[1] / 29 May 2019; 3 months ago[1] |
| Operating system | Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, previously also OS/2 and DOS |
| Platform | 64-bit (previously also 32-bit and 16-bit) x86 PCs |
| Available in | English, German, Hungarian, Chinese, Russian |
| Type | ECAD/EDA, CAM |
| License | subscription |
| Website | autodesk.com/products/eagle |
EAGLE is a scriptable electronic design automation (EDA) application with schematic capture, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, auto-router and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) features. EAGLE stands for Easily Applicable Graphical Layout Editor (German: Einfach Anzuwendender Grafischer Layout-Editor) and is developed by CadSoft Computer GmbH. The company was acquired by Autodesk Inc. in 2016.[2]
Features[edit]
EAGLE contains a schematic editor, for designing circuit diagrams. Schematics are stored in files with .SCH extension, parts are defined in device libraries with .LBR extension. Parts can be placed on many sheets and connected together through ports.
The PCB layout editor stores board files with the extension .BRD. It allows back-annotation to the schematic and auto-routing to automatically connect traces based on the connections defined in the schematic.
EAGLE saves Gerber and PostScript layout files as well as Excellon and Sieb & Meyer drill files. These are standard file formats accepted by PCB fabrication companies, but given EAGLE's typical user base of small design firms and hobbyists, many PCB fabricators and assembly shops also accept EAGLE board files (with extension .BRD) directly to export optimized production files and pick-and-place data themselves.
EAGLE provides a multi-window graphical user interface and menu system for editing, project management and to customize the interface and design parameters. The system can be controlled via mouse, keyboard hotkeys or by entering specific commands at an embedded command line. Multiple repeating commands can be combined into script files (with file extension .SCR). It is also possible to explore design files utilizing an EAGLE-specific object-oriented programming language (with extension .ULP).
History[edit]
The German CadSoft Computer GmbH was founded by Rudolf Hofer and Klaus-Peter Schmidinger in 1988 to develop EAGLE,[3][4][5][6] a 16-bit PCB design application for DOS. Originally, the software consisted of a layout editor with part libraries only. An auto-router module became available as optional component later on. With EAGLE 2.0 a schematics editor was added in 1991.[7] The software used BGI video drivers, and XPLOT to print.[7] In 1992, version 2.6 changed the definition of layers, but designs created under older versions (up to 2.05) could be converted into the new format using the provided UPDATE26.EXE utility.
EAGLE 3.0 was changed to be a 32-bit extended DOS application in 1994.
Support for OS/2Presentation Manager was added with version 3.5 in April 1996. This version also introduced multi-window support with forward-/backward-annotation, user-definable copper areas, and a built-in programming language with ULPs. It was also the first to no longer require a dongle.
In 2000 EAGLE version 4.0 officially dropped support for DOS and OS/2, but now being based on Qt 3[8][9] it added native support for Windows and was among the first professional electronic CAD tools available for Linux.[10] A 32-bit DPMI version of EAGLE 4.0 running under DOS was still available on special request in order to help support existing customers, but it was not released commercially. Much later in 2015, a special version of EAGLE 4.09r2 was made available by CadSoft to ease installation under Windows 7.
Starting with version 4.13, EAGLE became available for Mac OS X, with versions before 5.0.0 still requiring X11. Version 5.0.0 officially dropped support for Windows 9x and Windows NT 3.x/4.x. This version was based on Qt 4[11][12] and introduced user-definable attributes.
On 24 September 2009, Premier Farnell announced the acquisition of CadSoft Computer GmbH.[13][4]
Version 5.91.0 introduced an XML-based file format in 2011 but continued to read the older binary format. It could not, however, write files in the former format, thereby not allowing collaboration with EAGLE 5.12.0 and earlier. EAGLE 6.0.0 no longer supported Mac OS X on the Power PC platform (only on Intel Macs), and the minimum requirements were changed to Mac OS X 10.6, Linux 2.6 and Windows XP. This version also introduced support for assembly variants and differential pair routing with length matching and automatic meandering.
Version 7.0.0 brought hierarchical designs, a new gridless topological pre-router called 'TopRouter' for the conventional ripup-and-retry auto-router as well as multi-core support.[14] Version 7.3.0 introduced native 64-bit versions for all three platforms in 2015. Version 7.6.0 dropped support for the 32-bit Mac OS X version in 2016. EAGLE 6.x.x continues to read EAGLE 7.x.x design files for as long as the hierarchical design feature isn't used.[14]
On 27 June 2016, Autodesk announced the acquisition of CadSoft Computer GmbH from Premier Farnell, with Premier Farnell continuing to distribute CadSoft products for Autodesk.[15] Autodesk changed the license to a subscription-only model starting with version 8.0.0 in 2017. Only 64-bit versions remain available any more. The file format used by EAGLE 8.0.0 and higher is not backward compatible with earlier EAGLE versions.
License model[edit]
Since EAGLE version 8.0.0, there are Premium, Standard, Free, and Student & educator editions, with the Standard and Premium versions sold on a monthly or annual subscription basis, requiring online reactivation at least every 14 days (30 days since version 9.0).
Comparison of features for the various available editions:[16][17]
Eagle Pcb Layout Software Download
| Version | Schematic sheets | Layers | PCB size | Use | Cost/month | Cost/year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premium | 999 | 16 | 4 m² | Any | $65 | $510 |
| Student and educator | 999 | 16 | 4 m² | For student and educator use only | Free | Free |
| Standard | 99 | 4 | 160 cm² | Any | $15 | $100 |
| Free | 2 | 2 | 80 cm² | For individual, non-commercial use only | Free | Free |
For comparison, the former (no longer obtainable) perpetual licensing scheme for EAGLE 7.x.x with costs referring to the 2016 prices for a single-user license:[18]
| Version | Schematic sheets | Layers | PCB size | Use | Cost ('LS' without Autorouter) | Cost (with Autorouter) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate (LS) | 999 | 16 | 4 m² | Any | $1145 | $1640, €1385 |
| Premium (LS) | 99 | 6 | 160×100 mm² | Any | $575 | $820, €690 |
| Maker | 99 | 6 | 160×100 mm² | For individual, non-commercial use only | N/A | $169, €140 |
| Educational | 99 | 6 | 160×100 mm² | For non-commercial student and educator use only | N/A | Free |
| Standard | 2 | 2 | 100×80 mm² | Any | N/A | $69, €62 |
| Express | 2 | 2 | 100×80 mm² | For individual, non-commercial use only | N/A | Free |
Community[edit]
A large group of textual and video tutorials exists for beginners to design their own PCBs.[19]
The DIY electronics site SparkFun uses EAGLE and releases the EAGLE files for boards designed in-house. SparkFun Electronics[20] is a company that has grown due to the hobbyist market exemplified by Make magazine and others. Many of these companies offer EAGLE part libraries[21] which define schematic shapes, pinouts, and part sizes to allow for correct layout in the PCB layout editor.
And Subway Surfers is one the best game. Subway surfers game. It is a simple game which has easy navigation. Like moving up, left, right, and rolling on the ground. Therefore, any generation plays this game without difficulties.
Pcb Layout Software Comparison
Other popular libraries include Adafruit,[22]Arduino,[23] SnapEDA,[24] and Dangerous Prototypes,[25]element14 (a subsidiary of Farnell, former owners of CadSoft) also have some libraries available from their site.[26]
Using ULPs to convert EAGLE .BRD files into Specctra-compatible design files (with file extension .DSN) it is possible to export designs for usage in conjunction with advanced external autorouters such as KONEKT ELECTRA,[27]Eremex TopoR[28] or Alfons Wirtz's FreeRouting.[29] For further touching-up the finished designs in session format can be imported back into EAGLE via .SES to .SCR script file converters.
Eagle Pcb Design Software Tutorial
Controversies[edit]
In spring 1991 the dongle protection scheme of EAGLE 2.0 had been cracked causing a decline of 30% in sales, while sales for a reduced demo version with a printed manual saw a significant increase.[3] As a consequence in 1992 CadSoft sent thousands of floppy disks containing a new demo of EAGLE 2.6 to potential users, in particular those who had ordered the former demo but had not subsequently bought the full product.[3] The new demo, however, also contained spy code scanning the user's hard disk for illegal copies of EAGLE.[3] If the program found traces of such, it would show a message indicating that the user was entitled to order a free printed manual using the displayed special order code, which, however, was actually a number encoding the evidence found on the user's machine.[3] Users sending in the filled out form would receive a reply from CadSoft's attorneys.[3][30] The act of spying, however, was illegal as well by German law.[3][30]
In 2014, EAGLE 7.0.0 introduced a new FlexeraFLEXlm-based licensing model, which wasn't well received by the user community, so that CadSoft returned to the former model of independent perpetual licenses with EAGLE 7.1.0.
Despite announcements to the contrary in 2016, Autodesk switched to a subscription-only licensing model with EAGLE 8.0.0 in January 2017.[31][32] Without an online connection to a licensing server to verify the licensing status every two weeks (four weeks since version 9.0.0), the software would fall back to the functionality of the freeware version.[31][32] This caused an uproar in the user community, in particular among those who work in secure or remote environments without direct internet access and users for whom it is mandantory to be able to gain full access to their designs even after extended periods of time (several years up to decades) without depending on third-parties such as Autodesk to allow reactivation (who may no longer be around or support the product by then). Many users have indicated they would refuse to upgrade under a subscription model and rather migrate to other electronic design applications such as KiCad.[31][32]
See also[edit]
- Video Disk Recorder (VDR) – another software written by Klaus Schmidinger
References[edit]
- ^ abadmin (2019-05-29). 'RELEASE NOTES - Autodesk EAGLE version 9.4.2' (in English and German). Autodesk. Archived from the original on 2019-04-28. Retrieved 2019-05-30.
- ^'Sale of CadSoft'. Archived from the original on 2016-07-24. Retrieved 2016-07-07.
- ^ abcdefg'Trojanisches Pferd' [Trojan horse]. Der Spiegel (in German). SPIEGEL-Verlag Rudolf Augstein GmbH & Co. KG (36): 238, 242. 1992-08-31. Archived from the original on 2017-09-18. Retrieved 2017-09-18.[1]
- ^ abGoldbacher, Alfred (2009-10-02). 'CadSoft: Wie es weitergehen soll' (in German). ElektronikNet. Archived from the original on 2017-09-17. Retrieved 2017-09-17.
- ^Kuther, Margit (2013-11-25). 'PCB-Design: Wie wichtig sind Communities für PCB-Entwickler?'. Elektronik Praxis (in German). Archived from the original on 2017-09-17. Retrieved 2017-09-17.
- ^Siering, Peter (2015-02-19). 'Seiner Zeit voraus: Klaus Schmidingers Video Disk Recorder VDR' (in German). Heise online. Archived from the original on 2017-09-20. Retrieved 2017-09-20.
- ^ ab'Unterschiede zwischen EAGLE 1.3 und EAGLE 2.0' [Differences between EAGLE 1.3 and EAGLE 2.0]. EAGLE-Handbuch [EAGLE manual] (in German). CadSoft Computer. 1991. p. A-14.
- ^Schmidinger, Klaus (2001-10-03). 'Change Font nochmals'. eagle.betatest (in German). Archived from the original on 2017-10-05. Retrieved 2017-10-05.
- ^Schmidinger, Klaus (2003-05-08). 'Abgeschnittenes §-Zeichen'. eagle.betatest (in German). Archived from the original on 2017-10-05. Retrieved 2017-10-05.
- ^Dölle, Mirko (September 2004). 'Schwer auf Draht - Platinen-Layout-Programme Eagle Version 4.11 für Linux'. LinuxUser (in German). Archived from the original on 2017-09-20. Retrieved 2017-09-20.
- ^Schmidinger, Klaus (2007-09-24). 'EAGLE 4.9'. eagle.betatest. Archived from the original on 2017-10-05. Retrieved 2017-10-05.
- ^'Was ist neu in Version 5?'. CadSoft online (in German). CadSoft Computer GmbH. 2011. Version 5.10. Archived from the original on 2017-10-05. Retrieved 2017-10-05.
- ^Green, Harriet; Whiteling, Mark (2009-09-24). 'Acquisition of CadSoft Computer GmbH'. Premier Farnell plc. Archived from the original on 2017-09-17. Retrieved 2017-09-17.
- ^ abGoldbacher, Alfred (2014-10-01). 'Leiterplatten-Design-Software Eagle: Version 7 des Adlers ist gelandet' (in German). ElektronikNet. Archived from the original on 2017-09-22. Retrieved 2017-09-22.
- ^Buetow, Mike (2016-06-27). 'Autodesk Acquires Eagle from Cadsoft'. Printed Circuit Design & Fab. UP Media Group Inc. Archived from the original on 2017-09-17. Retrieved 2017-09-17.
- ^'Buy Autodesk EAGLE'. Autodesk. Retrieved 2017-02-17.
- ^'Eagle education or student version'. Autodesk. Retrieved 2017-02-17.
- ^'Find a plan that fits your needs'. CADSOFT EAGLE. Archived from the original on 2016-08-04. Retrieved 2016-08-04.
- ^'Turn Your EAGLE Schematic into a PCB'. Instructables.
- ^Seidle, Nathan (2008-06-19). 'Lecture 8 - EAGLE: Schematics'. SparkFun. Retrieved 2010-03-23.
- ^'Sparkfun Eagle Library'.
- ^'Adafruit library github page'. 2018. Retrieved 2018-10-14.
- ^'Arduino FAQ'.
- ^'SnapEDA Website'.
- ^'Dangerous Prototypes library'.
- ^'Element 14 EAGLE CAD Libraries'.
- ^'KONEKT Shape Based PCB Autorouting - ELECTRA PCB AutoRouting'. KONEKT. 2017. Archived from the original on 2017-09-24. Retrieved 2017-09-24.
- ^'TopoR Version History - What's New in TopoR version 6.2'. Eremex. 2017-09-24. Archived from the original on 2017-09-24. Retrieved 2017-09-24. (NB. Includes a list of new features since TopoR 3.0. TopoR 5.4.14203 (2012-12-21) introduced support for EAGLE: 'The Eagle BRD plain-text format is now supported. This format is used by files created in the Eagle 6.0 system.'. Improved in TopoR 5.4.14362 (2013-07-02): 'During import of Eagle BRD-files: in some cases the angle of rotation of pads was disregarded, in some cases the vias’ pad size was assigned incorrectly, sometimes the wires on the inner layers were disappearing.')
- ^Wirtz, Alfons (2014-03-08) [2004]. 'FreeRouting - Printed Circuit Board Routing Software from FreeRouting.net'. Archived from the original on 2017-09-24. Retrieved 2017-09-24.
- ^ abMöcke, Frank (1992). 'CadSoft rächt sich an Raubkopierern - Adressen aus bestem Hause'. c't - magazin für computertechnik (in German) (10): 16. Archived from the original on 2017-09-18. Retrieved 2017-09-18.
- ^ abcEvenchick, Eric (2017-01-19). 'Autodesk Moves EAGLE to Subscription Only Pricing'. HACKADAY. Archived from the original on 2017-09-19. Retrieved 2017-09-19.
- ^ abcGrannemann, Kathrin (2017-01-24). 'Autodesk Eagle: PCB-Software künftig nur im Abonnement'. Make: (in German). Media Maker GmbH. Heise ID -3605890. Archived from the original on 2017-09-19. Retrieved 2017-09-19.
Further reading[edit]
- Monk, Simon (2014-06-12). Make Your Own PCBs with EAGLE: From Schematic Designs to Finished Boards (1 ed.). McGraw-Hill Education / TAB Electronics. ISBN978-007181925-1.
- Scarpino, Matthew (2014-04-01). Designing Circuit Boards with EAGLE - Make High-Quality PCBs at Low Cost (1 ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN978-013381999-1.
- Duncan, Mitchell (2013). Eagle V6: Getting Started Guide - Learning to fly with EAGLE (1 ed.). Elektor-Verlag GmbH. ISBN978-190792020-2.
- Williams, Al (2003-10-15). Build Your Own Printed Circuit Board - Design to Production - Everything You Need to Make Your Own PCBs (1 ed.). McGraw-Hill Education / TAB Books. ISBN978-0-07-142783-8.
- Edwards, Lewin A. R. W. (2003). Embedded System Design on a Shoestring - Achieving High Performance with a Limited Budget. Newnes. ISBN978-0-7506-7609-0. (NB. Includes a copy of EAGLE 4.09r2.)
External links[edit]
- https://www.autodesk.com/products/eagle (Autodesk's EAGLE web support forums)
- news://news.cadsoft.de (CadSoft's EAGLE support newsgroups via NNTP)
- ftp://ftp.cadsoft.de/eagle/ (CadSoft's archive of old EAGLE versions)